
POST 1: AWARENESS
How bad is new invasive pest, Fall Armyworm?
Fall Armyworm (FAW) is an invasive species that arrived in Myanmar in 2018. After causing widespread crop destruction in Africa in 2016. It is now in India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand and China.
English Name: Fall Armyworm
Myanmar name: Fall Nga Myaung Taung
Scientific Name: Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith)
Characteristics of Fall Armyworm
- FAW has a white inverted “Y” mark on the front of the dark head.
- The easiest way to identify the FAW is through a set of four large spots that form a square on the upper surface of the last segment of its body.
- The pupa is reddish brown in color and a pair of spine at the end of the bod
- The adult moth is a strong flier. It can fly over 60 miles (100 km) per night in search of host plants.
Host Range
Fall Armyworm prefers maize, but can also feed on more than 80 species of crops such as rice, sugarcane, wheat, cotton and vegetables.
Symptoms
- Early stage larval feeding:
- Causes “windowpane” and shot holes in leaves
- Late stage larval feeding:
- Causes elongate, ragged holes
- May cut leaves in half
- Injures developing tassel in tasseling stage
- Plugs whorl with wet, yellowish-brown frass
Symptom-based treatment is very much important for FAW management because of two reasons; (i) the stage of symptom progression indicates the stage of larval growth, and (ii) the stage of larval growth decides the choice of control measure.
Download the Goldn Paddy Application by following this link www.goldenpaddy.com.mm to get the latest news on FAW.
POST 2: SCOUTING
How do you scout to prevent the fall Armyworm?
Early detection of Fall Armyworm infestations requires timely and regular field scouting.
Scouting should begin soon after seedling emergence.
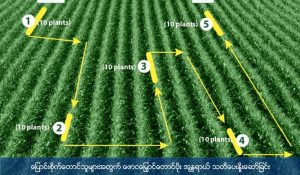
Scouting Methods
- The scout walks 5 meters into the maize field (avoiding the border rows or edge of the field is important).
- The scout then zigzags (“W” pattern) the field, stopping at 5 different locations.
- At each of these locations the scout assesses 10 – 20 plants looking for signs of FAW feeding. It is important to note that FAW caterpillars hide inside the maize whorl during the day so check the whorl thoroughly.
- The percentage of damaged plants is recorded and the scout moves to the next checkpoint (next point in “W” pattern).
- After scouting 5 locations in the field, calculate the total percent (%) infestation across the field. Do this by dividing the total number of infected plants by all the plants you have scouted and then multiply by 100.
- Refer to the FAW knowledge section of Golden Paddy Mobile Application to see what the action thresholds are for each growth stage and read if and what treatment is recommended.
Download the Golden Paddy Application by following this link www.goldenpaddy.com.mm to get the latest news on FAW.

POST 3: TREATMENT
How to Control Fall Armyworm
In this post we provide a list of the control methods that are recommended by the Department of Agriculture (DOA), International Fertilizer Development Centre (IFDC) and other chemical companies to control Fall Armyworm.
Most of the retailers in your area are also trained by DOA, IFDC and other chemical companies on these control methods (pesticides).
In the Golden Paddy application you can find an updated list of products. They also have a list of retailers for Shan State who are trained with this knowledge.
Download the Golden Paddy Application by following this link www.goldenpaddy.com.mm to access the retailers’ data and get the latest news on FAW.
Spray Pesticides Sequence
- Crop Stage: Seedling to 2 weeks
Action threshold: First catch 3moths /trap
: 5% infected plants
Spray Sequence:
- t (Bacillus thuringiensis)
- Neem
- Emamectin benzoate
- Chlorfenapyr 10 % SC
- Chlorantraniliprole
- Crop Stage: 2-4 weeks old
Action threshold: 5-10% infected plants
Spray Sequence:
- t (Bacillus thuringiensis) (first spray)
(Second Spray pesticides listed)
- Emamectin benzoate
- Emamectin benzoate +lambda chyhalothrin
- Chlorfenapyr 10 % SC
- Flubendiamide
- Chlorantraniliprole
- Indoxacarb
- Crop Stage: 4 -7 weeks old
Action threshold: 10 – 20% infected plants
Spray Sequence:
(First Spray any pesticides listed)
- Emamectin benzoate
- Emamectin benzoate +lambda chyhalothrin
- Chlorfenapyr 10 % SC
- Flubendiamide
- Chlorantraniliprole
- Indoxacarb
- Thiodicarb (OP)
- Crop Stage: 7 week to Tasseling
Action threshold: > 20% infected plants
Spray Sequence:
(First Spray any pesticides listed and alternate the pesticide for second spray)
- Emamectin benzoate
- Emamectin benzoate +lambda chyhalothrin
- Chlorfenapyr 10 % SC
- Flubendiamide
- Chlorantraniliprole
- Indoxacarb
- Crop Stage: Tasseling to harvest
Action threshold: 10% ear damage
No pesticide application, but manually pick and destroy larvae.



